Different ways to turn the radio into a metal detector
The first method:
It consists of the transmitter, which is the transmitter used in the sufficient detector device, which in turn consists of two transistors for transmission, where the first transistor with the first coil sends an electromagnetic signal with the same value as the signal sent by the second transistor with the second coil, and here we control the signal through a variable capacitor or two variable capacitors on the first coil Or on both the first and second coils, and this method consists of a transistor number (2), a capacitor 104 number (8), a capacitor of 220 microns, and a resistance of 10 kilo ohms number (4). variable to tune the signal.
The second method:
This is done through one oscillator of the npn type with two capacitors No. 104 and a capacitor 220 micro in addition to a resistance of 10 kilo ohms number 4, where the oscillator sends a frequency close to 100 kilohertz to the coil and the radio antenna and the radio negative are connected to both ends of the coil and thus through the balance in the radio We can get the signal, and when the metal approaches the coil, a sound is produced, which is the difference between the radio frequency and the transistor frequency transmitted in the circuit.
What is an oscillator:
It is a three-crystal electronic piece interconnected with each other, as two of them are of the same type on the sides and the third is in the middle and they differ in type. The transistor was invented by the two American scientists Brattinian and Bardeen in 1948. From knowing everything related to the transistor before dealing with it to get the desired result and avoid any mistakes that can be made when connecting, such as knowing the components of the transistor, the method of connecting wires, and using the appropriate type of transistor. How a Transistor Works An NPN transistor is designed to pass electrons from the emitter to the collector. The emitter sends electrons to the base, which in turn controls the coming from the emitter. Most of the electrons sent from the emitter are collected by the collector, which in turn sends them to the next part of the circuit. As for the PNP transistor, it works in the same way, but in the opposite direction, as the base controls the passing current, and this current goes in the opposite direction, meaning that it goes from the emitter to the collector, and the emitter sends gaps, which are a significant expression of an empty place that had removed an electron instead of sending electrons and then Gathered in the collector, and the transistor acts as a kind of valve for the electrons, and also the tip of the base can be likened to a handle that adjusts to control increasing or decreasing the number of electrons flowing from the emitter to the collector, and perhaps at the beginning when connecting the wires errors occur in the wire connections that make the transistor spend a lot of heat, You may burn many transistors before success.
Oscillator Components:
Base: It is a carbon material that contains four electrons in the valence orbit mixed with boron that contains three electrons in the valence orbit. This type is symbolized by the letter P. The size of the base in the transistor is twice the other two sides. So it occupies the largest part of the transistor.
Collector: It is carbon, but it carries five electrons in the valence field with arsenic. Which makes the composition of the molecule in which it is more than stable, and this does not negate the fact that it is positive, as the substance did not lose or gain anything from its electrons, so it is neutral, and this type is symbolized by the letter N.
Emitter: It differs from the collector in the presence of elements only in a very different density of arsenic.
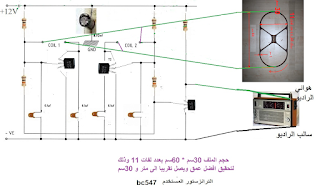
The third method: This method is based on making a circuit with three transistors, the first and second transistors and their components, as we mentioned in the previous method. And a quarter for the large metal, and connect the output of the third transistor synthesizer to the antenna terminal of the radio, and the negative of the circuit to the negative of the radio.
Follow the video with us





Comments